The Utilization of RFA Assessments for Early (Anytime) Loading in the Maxillary Posterior Area
- Dr. Chonghwa Kim

- Nov 19, 2015
- 2 min read
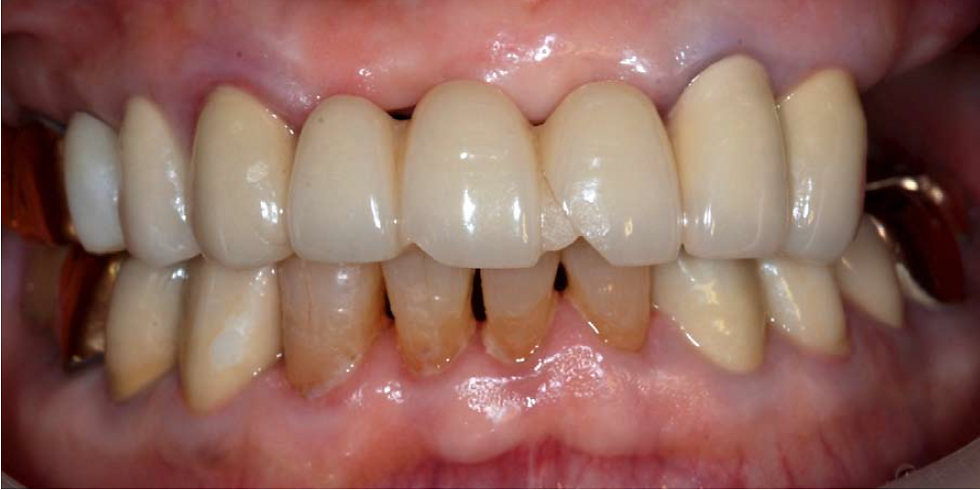
A 74 year old male patient presents to our clinic with a chief complaint, “I want to be able to chew on my left side, but I only have about a month before my trip to States. I can’t chew that well on my right side either. If you can fix my left fast & good, I will come back to you again for my right side in six months. How’s that sound?”

The patient reports the posterior teeth in maxillary left quadrant have been extracted by his previous dentist about 6 weeks ago. The height of remaining alveolar bone was assessed to be appropriate for implant placement.
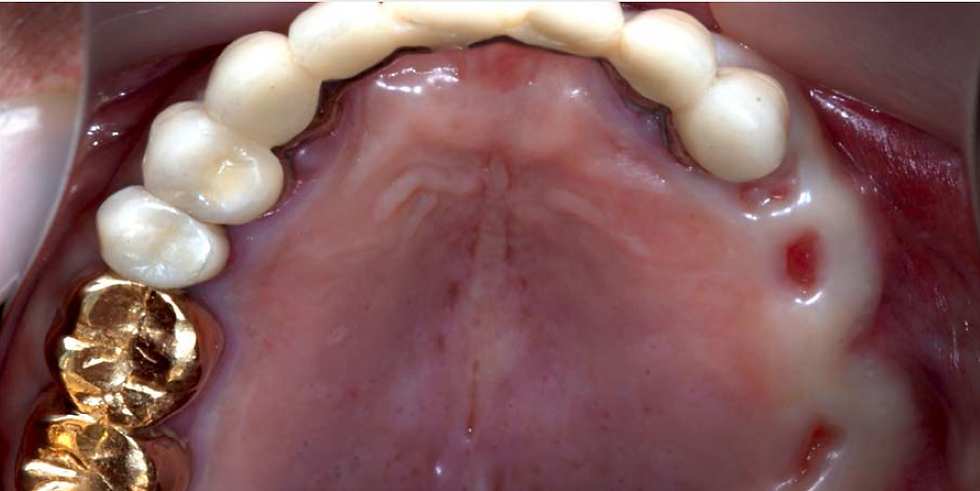
The width of remaining alveolar ridge was acceptable for implant placement as well but the soft tissue was not quite complete at this time.

3 day post-op view. Three implants were placed at the 1st & 2nd premolar, and the 2nd molar site. The 1st molar site was avoided due to the presence of severe bony defect on buccal side. (indicated with an black arrow) 1st & 2nd surgery were performed simultaneously and modified (narrow) healing abutments were connected to ease suturing and expedite soft tissue healing.

1 week post-op view. The healing abutments were now changed with wider diameter ones.
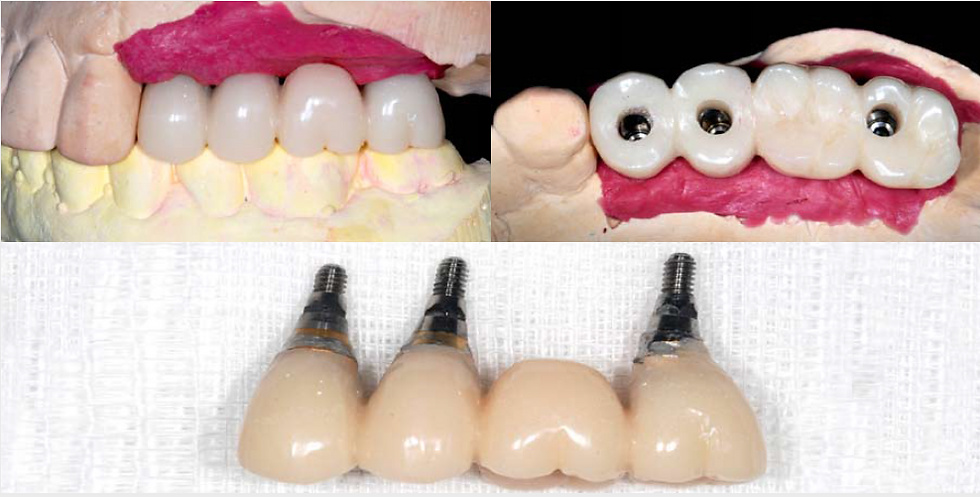
A 1-unit screw-retained provisional restoration was fabricated to avoid cementation of the provisional restoration. This enables better peri-implant tissue response during healing process. The ‘SCRP’ abutments (prefabricated abutment with semi-hexa connection) were used to ensure the insertion path of the restoration.

The provisional restoration was delivered on 8th day post-op.
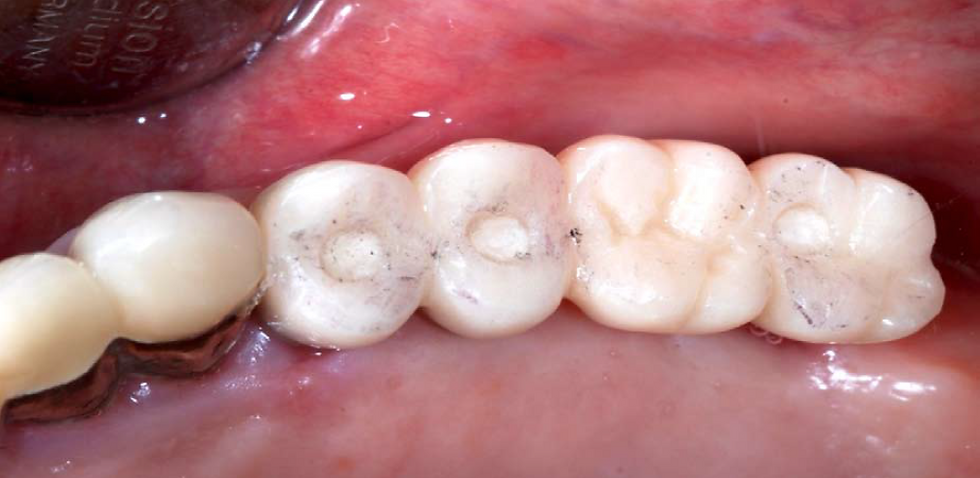
Occlusal view

Panoramic view of the provisional restoration
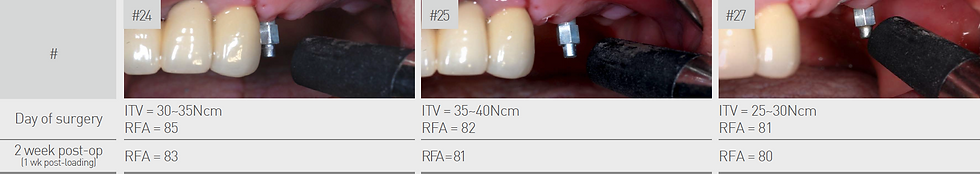
The ITV (Insertion Torque Value)’s and RFA (Resonance Frequency Analysis) values for each site were assessed and recorded on the day of surgery and 2 week post-op (1 week post-loading). No significant drop or decrease in RFA value was observed after a week of loading.

A gap between the bottom surface of the pontic and the soft tissue below was noticed as the soft tissue healing continues.(indicated with an black arrow)

The new soft tissue contour of the pontic site was recorded unto the provisional restoration with the direct use of acrylic resin intraorally (upper left & right) and trimmed (lower left & right, indicated with blue arrows).

Using the recontoured provisional restoration, the master cast (used for the fabrication of provisional restoration) was altered to avoid an additional impression for final restoration. The gum mask on the master cast was trimmed according to the new contour of the pontic. (indicated with blue arrows)

The final restorations, a single restoration for #24 and a 3-unit FPD for #25-27, were fabricated and delivered in 4 weeks.

Final restorations on the working cast.
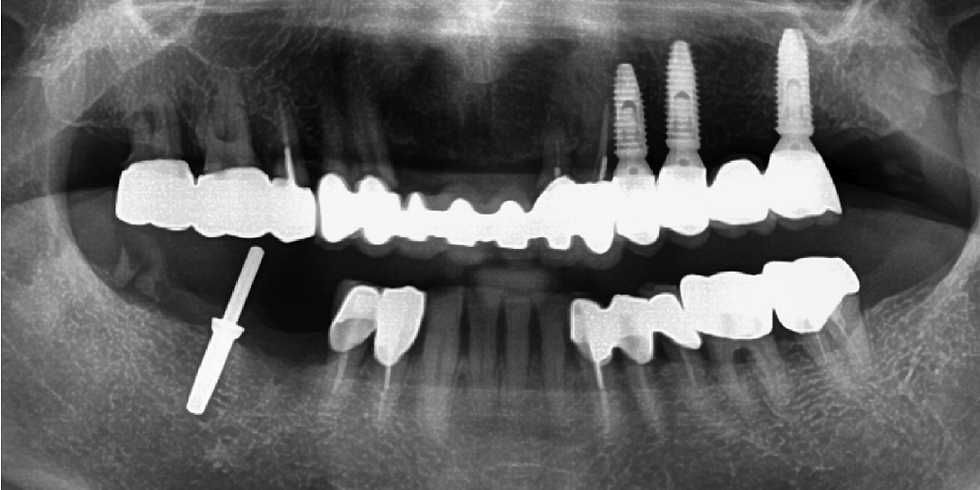
Post-delivery panoramic view.



Comments